by Murray Gonzalez
This article is provided for organizations needing a framework to implement the ISO 9001:2015 standard to mesh with the Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle to continually improve their system.
ISO 9001:2015 was revised for many reasons. The International Organization for
Standardization (ISO) cited the needs driving those changes:
- adapt to a changing world
- reflect the complex environments in which organizations operate
- provide a consistent foundation for the future
- ensure the new standard reflects the needs of all relevant interested parties
- ensure alignment with other management system standards1
A new common clause structure has been developed. Key benefits of the common clause structure:
- All ISO management system standards will look the same with the same structure (some deviations)
- More efficient to address multiple management system requirements (e.g., ISO 9001 and ISO 14001)
- Provides the option of integrating management systems
- Standardized core definitions Ibid
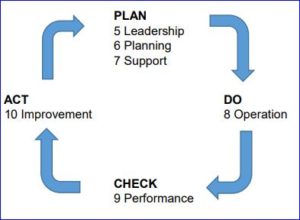
The common clause structure is organized into the following ten clauses:
1 Scope
2 Normative references
3 Terms and definitions
4 Context of the organization
5 Leadership
6 Planning
7 Support
8 Operation
9 Performance
10 Improvement Ibid
The Deming Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle (PDCA), is a model, consisting of
the following steps:
Plan – The Plan step involves identifying a goal or purpose, formulating a theory, defining
success metrics and putting a plan into action.
Do – The Do step is when the components of the plan are implemented, such as making the
product or providing the service.
Check – The Check step, often referred to as the Study step, is where outcomes are monitored
to test the validity of the plan for signs of progress and success, or problems and areas for
improvement.
Act – The Act step closes the cycle, integrating the learning generated by the entire process,
which can be used to adjust the goal, change methods or even reformulate a theory altogether.
These four steps of the PDCA Cycle are repeated over and over as part of a never-ending cycle
of continual improvement.2
The new ISO 9001:2015 management system standard clauses can be overlaid with the PDCA
cycle to work in conjunction with each other as follows:
The information presented herein broadly shows the ISO 9001:2015 system and the PDCA
Cycle design to align and work together. The details are in the sub clauses. Each organization
needs to adjust their quality management system to fit within the parameters of its own situation.
REFERENCES
1 ISO 9001:2008 to ISO 9001:2015 Summary of Changes ISO/TC/176/SC 2/N1267
2 The PDSA Cycle, The W. Edwards Deming Institute 2016
MURRAY GONZALEZ is the Marketing Manager with QualityWBT. He has over 25 years of experience as a quality manager, production manager, and as a marketing manager. Gonzalez has a Master’s in Industrial-Organizational Psychology and a certification in Organizational Development/Leadership from the University of West Florida. He is an ASQ Certified Biomedical Auditor and a Certified Six Sigma Green Belt. Gonzalez is an active ASQ member serving as the Region 15B Deputy Regional Director, and as the ASQ Certification Recertification Chair, the Programs Chair, and the Publicity Chair with Pensacola, Florida Section 1507.